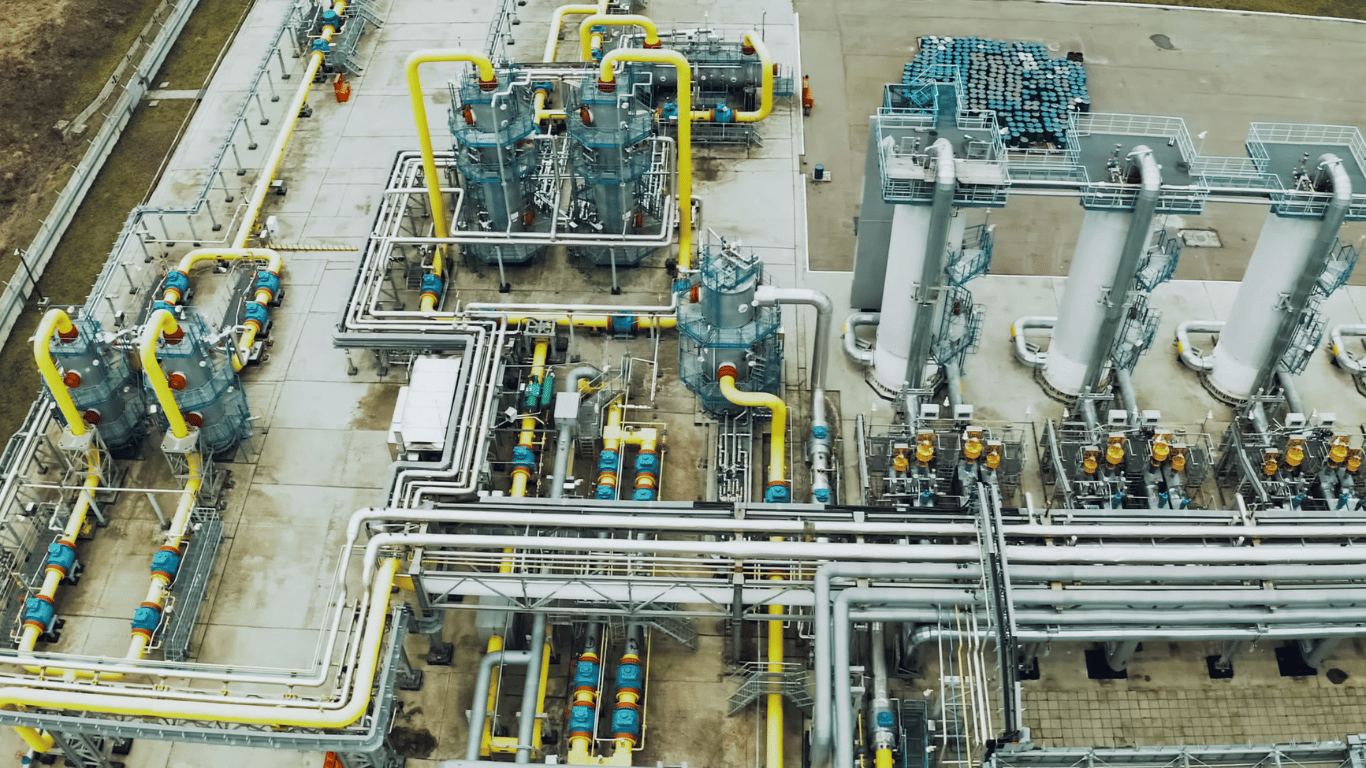
Industrial Process Solutions
Industrial process solutions encompass a wide range of technologies, systems, and services designed to optimize, automate, and enhance various industrial operations. These solutions are essential for improving efficiency, safety, and productivity in industries such as manufacturing, chemical processing, oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and more. Here’s an overview of what industrial process solutions might include:
1. Automation and Control Systems
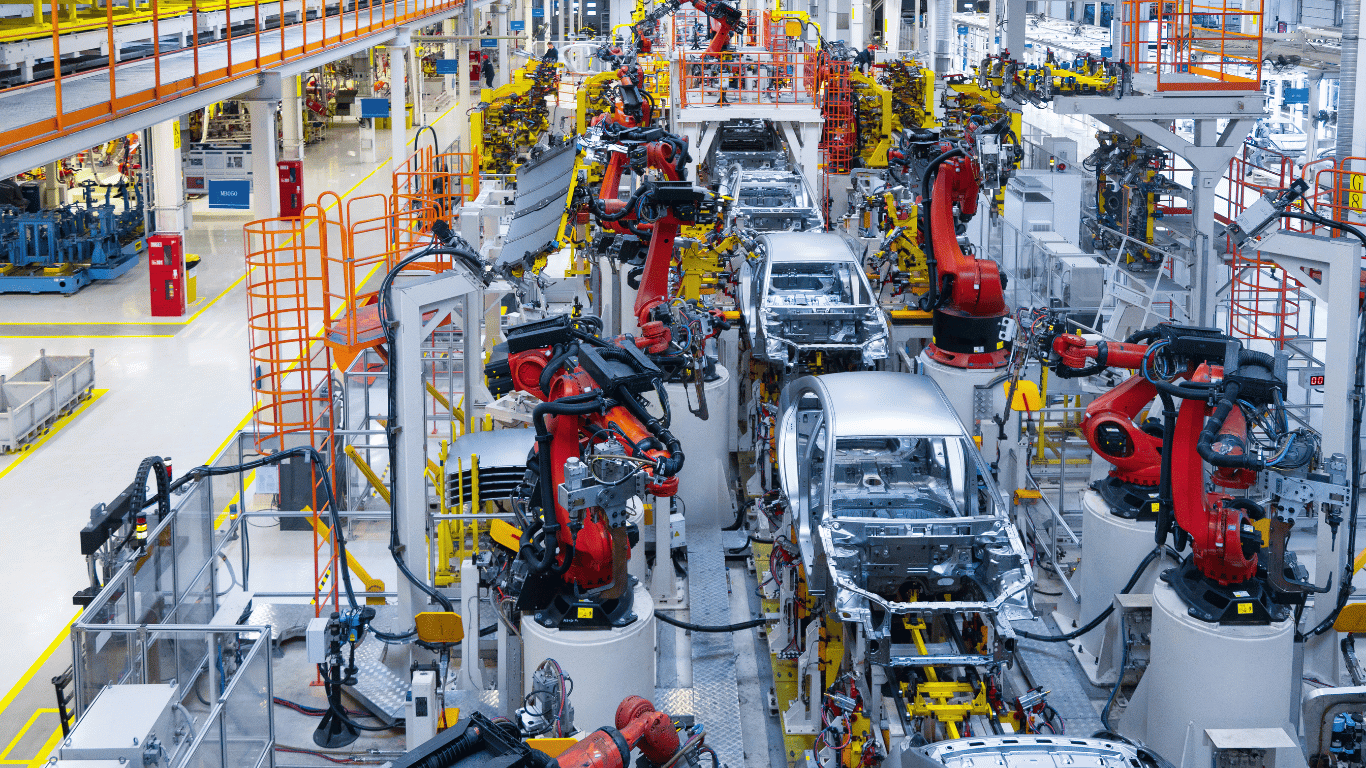

- PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers): Used to control machinery and processes.
- SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition): Systems for real-time data monitoring and control.
- DCS (Distributed Control Systems): Automation systems for complex, large-scale processes.
- HMI (Human-Machine Interface): Interfaces that allow operators to interact with machines.
2. Process Optimization
- Advanced Process Control (APC): Techniques to enhance process performance.
- Lean Manufacturing: Methods to reduce waste and improve efficiency.
- Six Sigma: A set of techniques for process improvement and quality management.
3. Process Equipment and Machinery
- Pumps, Valves, and Compressors: Essential components for fluid handling and process control.
- Heat Exchangers: Devices for transferring heat between different fluids.
- Mixers and Reactors: Equipment for chemical processing and material synthesis.
4. Safety and Compliance
- Industrial Safety Systems: Fire and gas detection, emergency shutdown systems.
- Environmental Control: Solutions for pollution control, waste management, and regulatory compliance.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Safety gear for workers in hazardous environments.
5. Data Analytics and IoT Integration
- Predictive Maintenance: Using data to predict equipment failures before they happen.
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): Connecting machinery and sensors to collect and analyze data.
- Big Data Analytics: Analyzing large datasets to optimize processes and make informed decisions.
6. Energy Management
- Energy Efficiency Solutions: Technologies to reduce energy consumption.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Incorporating solar, wind, and other renewable sources into industrial processes.
- Cogeneration: Simultaneous production of electricity and useful heat.
7. Material Handling and Logistics
- Conveyor Systems: For moving materials within a facility.
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): Robots for material transport.
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Software for managing inventory and logistics.
8. Maintenance and Reliability
- CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems): Software for tracking maintenance activities.
- Condition Monitoring: Techniques for assessing the health of machinery.
- Root Cause Analysis: Identifying the underlying causes of equipment failures.
9. Custom Engineering Solutions
- Turnkey Projects: Complete process solutions from design to implementation.
- Custom Equipment Fabrication: Tailored equipment to meet specific process requirements.
- Process Simulation: Virtual modeling of processes to test and optimize designs.
10. Sustainability Initiatives
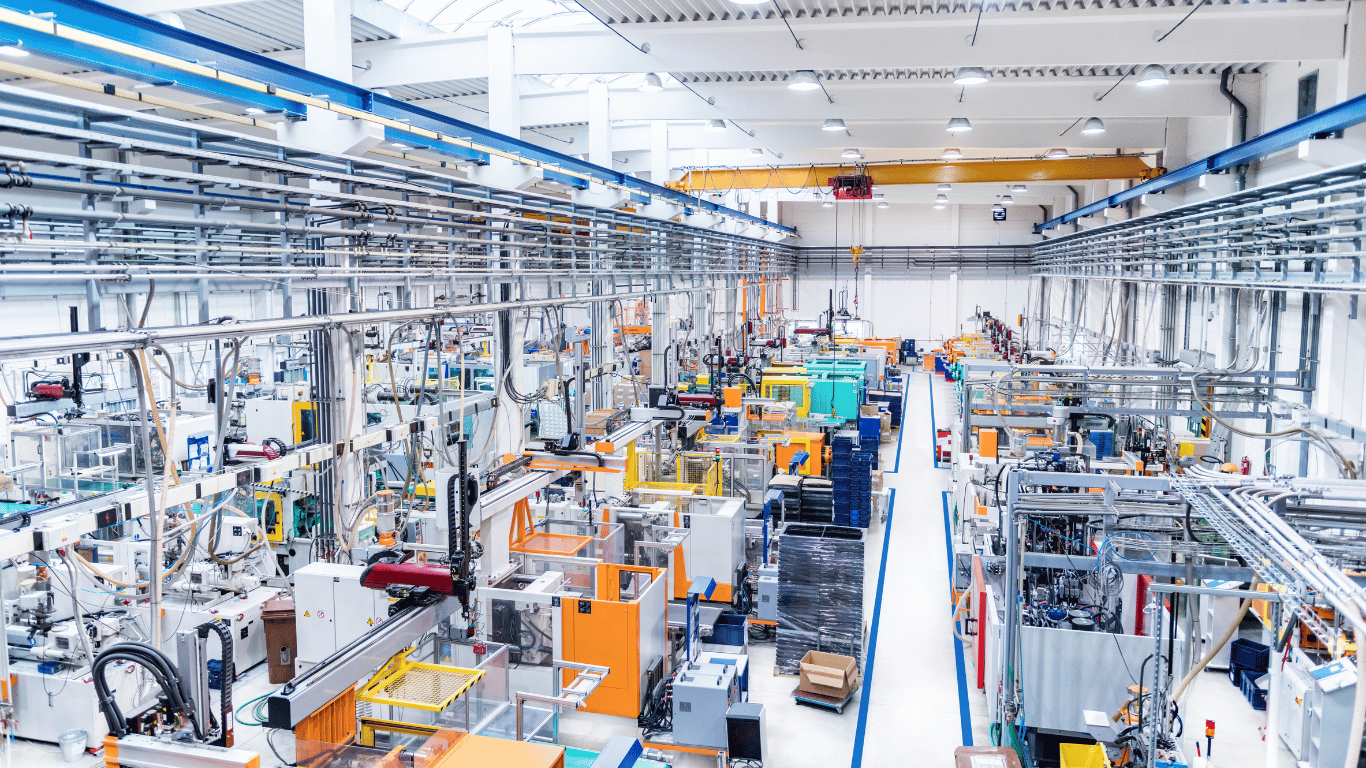
- Green Manufacturing: Implementing eco-friendly practices in production.
- Waste Reduction: Techniques for minimizing waste and recycling materials.
- Water Management: Efficient use and treatment of water in industrial processes.
Industrial process solutions are integral to modern industry, enabling companies to stay competitive by improving their operations, reducing costs, and adhering to regulatory requirements.
II. Benefit of Industrial Process Solutions
Industrial process solutions offer a wide range of benefits that significantly impact the efficiency, safety, and profitability of industrial operations. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Increased Efficiency of Industrial Process Solutions
- Optimized Operations: Industrial process solutions streamline and automate processes, reducing the time and effort required to complete tasks, thereby increasing overall efficiency.
- Reduced Downtime: Predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring minimize unplanned downtime by identifying potential issues before they lead to equipment failure.
- Energy Efficiency: By optimizing energy use and integrating renewable energy sources, companies can reduce energy consumption and lower operational costs.
2. Enhanced Safety of Industrial Process Solutions
- Improved Worker Safety: Automation and advanced safety systems reduce the need for human intervention in hazardous environments, lowering the risk of accidents.
- Compliance with Regulations: Industrial process solutions help ensure that operations adhere to safety and environmental regulations, avoiding fines and legal issues.
3.Industrial Process Solutions Cost Reduction
- Lower Operational Costs: Automation, process optimization, and energy management lead to significant cost savings by reducing waste, improving resource utilization, and minimizing labor costs.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Predictive maintenance and condition monitoring extend equipment life and reduce the frequency and cost of repairs.
4. Improved Product Quality
- Consistency and Precision: Automated control systems maintain consistent production parameters, leading to higher-quality products with fewer defects.
- Quality Control: Real-time data monitoring and analytics enable continuous quality control, ensuring that products meet required standards.
5. Greater Flexibility
- Adaptability to Market Changes: Industrial process solutions enable companies to quickly adapt to changes in demand, product specifications, and production volumes.
- Customization: Process solutions can be tailored to specific industry needs, allowing for customized production runs and the development of specialized products.
6. Data-Driven Decision Making
- Real-Time Insights: Integration of IoT and data analytics provides real-time data on process performance, enabling informed decision-making and rapid response to issues.
- Predictive Analytics: By analyzing historical data, companies can predict trends, optimize processes, and make proactive adjustments.
7. Environmental Sustainability
- Reduced Waste and Emissions: Process optimization and environmental control systems help minimize waste generation and reduce emissions, contributing to environmental sustainability.
- Resource Conservation: Efficient use of resources, such as water and raw materials, reduces the environmental footprint of industrial operations.
8. Scalability
- Growth Facilitation: Industrial process solutions can be scaled to accommodate business growth, whether expanding production capacity or entering new markets.
- Modular Solutions: Many solutions are modular, allowing companies to add or upgrade components as needed without overhauling the entire system.
9. Innovation and Competitiveness
- Enhanced Innovation: With advanced technologies and process solutions, companies can develop new products and processes, staying ahead of competitors.
- Market Differentiation: Superior process efficiency, product quality, and sustainability practices can be key differentiators in the marketplace.
10. Improved Customer Satisfaction
- Consistency in Deliverables: Consistent production quality and on-time delivery lead to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Responsive Supply Chain: Efficient processes enable quicker response to customer demands, improving service levels and reducing lead times.
Overall, industrial process solutions are vital for companies looking to improve their operations, reduce costs, enhance safety, and maintain a competitive edge in today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape.
III. Key Components of Industrial Process Solutions
1. Automation and Control Systems
- PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers):
- PLCs are specialized computers used to control machinery and processes in real-time. They are highly reliable, programmable, and capable of executing complex logic to manage tasks such as starting and stopping motors, opening and closing valves, and monitoring sensors.
- SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition):
- SCADA systems are used for real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes. They collect data from sensors and devices across a facility, allowing operators to monitor conditions, control equipment remotely, and respond to alarms. SCADA systems are crucial for large-scale processes where centralized control is needed.
- DCS (Distributed Control Systems):
- DCS are control systems that distribute control functions across multiple, interconnected systems rather than relying on a single, centralized controller. This decentralized approach enhances reliability and efficiency in complex industrial processes, such as chemical plants or power generation facilities.
- HMI (Human-Machine Interface):
- HMI refers to the user interface that allows operators to interact with the machinery and systems they control. HMIs display data from processes, provide controls for managing operations, and often include graphical interfaces to make monitoring and control more intuitive.
2. Process Optimization Tools
- Advanced Process Control (APC):
- APC involves the use of sophisticated algorithms and control strategies to optimize the performance of industrial processes. It goes beyond basic control systems by adjusting process variables to maintain optimal conditions, improving efficiency, reducing variability, and enhancing product quality.
- Lean Manufacturing:
- Lean manufacturing is a methodology focused on minimizing waste within manufacturing systems while maximizing productivity. This approach involves streamlining processes, reducing downtime, improving workflow, and eliminating non-value-added activities, all of which contribute to more efficient operations.
- Six Sigma:
- Six Sigma is a data-driven approach to process improvement that seeks to reduce defects and variability in manufacturing processes. It uses statistical methods to identify and eliminate causes of errors, improving quality and consistency. The methodology also emphasizes continuous improvement through the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) framework.
3. Essential Process Equipment
- Pumps:
- Pumps are essential for moving fluids (liquids, gases, slurries) through industrial processes. They come in various types, including centrifugal, positive displacement, and diaphragm pumps, each suited for different applications based on fluid characteristics and process requirements.
- Valves:
- Valves control the flow of fluids by opening, closing, or partially obstructing pathways within a system. They are crucial for regulating pressure, flow rates, and ensuring safe operation. Common types include gate valves, ball valves, and butterfly valves.
- Heat Exchangers:
- Heat exchangers transfer heat between two or more fluids without mixing them. They are used in processes where temperature control is critical, such as heating, cooling, or energy recovery applications. Types include shell-and-tube, plate, and air-cooled heat exchangers.
- Mixers:
- Mixers are used to blend, emulsify, or homogenize materials in industrial processes. They are essential in industries like chemical processing, food production, and pharmaceuticals. Different designs, such as paddle mixers, ribbon mixers, and high-shear mixers, are chosen based on the material properties and process requirements.
4. Safety Systems
- Fire and Gas Detection Systems:
- These systems are designed to detect and alert operators to the presence of fire or hazardous gases in an industrial environment. They typically include sensors, alarms, and control panels that trigger safety protocols, such as shutting down equipment or activating fire suppression systems.
- Emergency Shutdown Systems (ESD):
- ESD systems are critical for ensuring the safety of industrial processes by automatically shutting down equipment or entire systems in response to unsafe conditions. These systems are often integrated with other safety devices, such as pressure relief valves and fire detection systems, to prevent accidents and protect personnel and equipment.
5. Data Analytics and IoT Integration
- Predictive Maintenance:
- Predictive maintenance uses data analytics to predict when equipment is likely to fail, allowing for maintenance to be performed just in time to prevent unplanned downtime. This approach relies on sensors, machine learning algorithms, and historical data to monitor equipment health and predict failures before they occur.
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT):
- IIoT refers to the network of interconnected devices and sensors in industrial environments that collect and exchange data. This connectivity enables real-time monitoring, data-driven decision-making, and automation of processes. IIoT enhances efficiency, safety, and productivity by providing insights into equipment performance and process conditions.
- Big Data Analytics:
- Big data analytics involves analyzing large volumes of data generated by industrial processes to identify patterns, trends, and insights. This analysis helps in optimizing operations, improving product quality, and making informed decisions. By leveraging big data, companies can gain a competitive edge through enhanced operational intelligence.
IV. Industrial Process Solutions Target audiences
The target audiences for industrial process solutions are diverse, encompassing various roles, industries, and sectors that benefit from optimized and automated industrial processes. Here’s a breakdown of the primary target audiences:
1. Manufacturing Companies
- Industries: Automotive, electronics, consumer goods, aerospace, textiles, etc.
- Roles:
- Plant Managers: Interested in solutions that improve efficiency and reduce downtime.
- Production Engineers: Focus on process optimization and equipment performance.
- Quality Assurance Teams: Need solutions that ensure consistent product quality.
2. Oil & Gas Industry
- Industries: Upstream, midstream, and downstream operations.
- Roles:
- Operations Managers: Seek solutions for safety, compliance, and efficiency in complex processes.
- Safety Officers: Prioritize safety systems and environmental controls.
- Maintenance Teams: Focus on predictive maintenance and reliability of critical equipment.
3. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Companies
- Industries: Chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology.
- Roles:
- Process Engineers: Look for solutions to optimize chemical reactions and production processes.
- Regulatory Compliance Officers: Ensure adherence to stringent industry regulations.
- Research & Development Teams: Interested in innovative process solutions to accelerate product development.
4. Energy and Utilities
- Industries: Power generation, water treatment, renewable energy.
- Roles:
- Energy Managers: Focus on energy efficiency and integration of renewable energy sources.
- Operations Supervisors: Need reliable process control systems for continuous operation.
- Environmental Compliance Officers: Ensure processes meet environmental regulations.
5. Food and Beverage Industry
- Industries: Food processing, beverage production, packaging.
- Roles:
- Production Managers: Seek solutions to enhance process efficiency and ensure product safety.
- Quality Control Teams: Need to maintain consistent quality standards and adhere to food safety regulations.
- Supply Chain Managers: Focus on efficient material handling and logistics.
6. Mining and Metals Industry
- Industries: Mining operations, metal processing, smelting.
- Roles:
- Mining Engineers: Require robust process solutions for extraction and processing.
- Safety Managers: Focus on reducing risks in hazardous environments.
- Environmental Managers: Look for solutions that minimize the environmental impact of operations.
7. Pulp and Paper Industry
- Industries: Pulp production, paper manufacturing, packaging.
- Roles:
- Process Control Engineers: Seek solutions for optimizing the production process and reducing waste.
- Sustainability Managers: Interested in energy-efficient and environmentally friendly processes.
- Maintenance Teams: Need reliable equipment and predictive maintenance solutions.
8. Infrastructure and Construction
- Industries: Construction, infrastructure development, civil engineering.
- Roles:
- Project Managers: Require process solutions that ensure timely completion and cost efficiency.
- Construction Engineers: Focus on precision, safety, and efficiency in building processes.
- Safety Inspectors: Ensure compliance with safety standards and regulations.
9. Defense and Aerospace
- Industries: Military, aerospace manufacturing, defense contractors.
- Roles:
- Defense Engineers: Look for advanced process solutions to meet stringent defense industry standards.
- Quality Assurance Teams: Ensure that products meet high-quality and safety requirements.
- Operations Managers: Focus on optimizing production for complex, high-precision components.
10. Government and Regulatory Bodies
- Industries: Environmental agencies, occupational safety, regulatory compliance.
- Roles:
- Regulatory Inspectors: Need solutions that help enforce safety and environmental regulations.
- Policy Makers: Interested in promoting the adoption of sustainable and efficient industrial processes.
- Public Health Officials: Focus on ensuring that industrial processes do not harm public health.
11. Engineering and Consulting Firms
- Industries: Industrial consulting, engineering design, process optimization services.
- Roles:
- Consultants: Provide expertise and recommend process solutions to clients across industries.
- Engineers: Design and implement customized process solutions for various industrial applications.
- Project Managers: Oversee the deployment of industrial process solutions and ensure successful project delivery.
Each of these audiences has specific needs and priorities, which industrial process solutions can address by enhancing efficiency, safety, and compliance while reducing costs and environmental impact.
VI. Industrial process solutions Standards and Regulations
Industrial process solutions must adhere to various standards and regulations to ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance with local, national, and international laws. These standards and regulations vary by industry, region, and specific application but generally cover aspects such as safety, environmental protection, quality, and operational efficiency. Below are some of the key standards and regulations relevant to industrial process solutions:
1. Safety Standards
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration):
- Applicable in the United States, OSHA sets standards for workplace safety, including machinery operation, electrical safety, and hazardous materials handling.
- IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission):
- Provides international safety standards for electrical equipment and systems, including industrial automation and control systems (e.g., IEC 61508 for functional safety).
- NFPA (National Fire Protection Association):
- Sets standards for fire safety in industrial settings, including guidelines for fire detection, suppression systems, and electrical safety (e.g., NFPA 70E for electrical safety).
- ANSI (American National Standards Institute):
- Publishes safety standards for machinery, personal protective equipment (PPE), and other industrial processes.
2. Environmental Regulations
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency):
- In the U.S., the EPA sets regulations for air and water quality, hazardous waste management, and emissions control, which industrial processes must comply with.
- ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems):
- An international standard for creating and maintaining an effective environmental management system (EMS) to minimize environmental impact.
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals):
- A European Union regulation that addresses the production and use of chemical substances, with a focus on human health and environmental safety.
- Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act:
- U.S. regulations that set limits on emissions and discharges into the air and water, affecting industrial processes.
3. Quality Standards
- ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems):
- An international standard that outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS), ensuring consistent product quality and continuous improvement.
- GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices):
- Applicable to the pharmaceutical, food, and medical device industries, GMP regulations ensure that products are consistently produced and controlled to quality standards.
- ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers):
- Sets standards for the design, construction, and testing of mechanical equipment, including pressure vessels, boilers, and piping systems (e.g., ASME BPVC).
4. Process Safety Standards
- API (American Petroleum Institute):
- Provides standards and best practices for the oil and gas industry, including process safety management, equipment design, and operational safety.
- ISA (International Society of Automation):
- Publishes standards for process automation and control systems, including safety instrumented systems (SIS) and cybersecurity (e.g., ISA/IEC 62443).
- PSM (Process Safety Management):
- OSHA’s standard (29 CFR 1910.119) for managing highly hazardous chemicals, focusing on preventing accidental releases of substances that could cause serious harm.
5. Electrical and Electronic Standards
- IEC 61000 (Electromagnetic Compatibility):
- Standards for ensuring that industrial electronic devices do not emit excessive electromagnetic interference (EMI) and are resistant to EMI from other sources.
- NEC (National Electrical Code):
- A U.S. standard published by NFPA for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment in various industrial settings.
6. Cybersecurity Standards
- NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology):
- Provides guidelines for cybersecurity in industrial control systems, including risk management and protection against cyber threats (e.g., NIST Cybersecurity Framework).
- ISA/IEC 62443:
- A series of standards specifically for securing industrial automation and control systems against cyber threats.
7. Industry-Specific Regulations
- FDA (Food and Drug Administration):
- Regulates the pharmaceutical, food, and medical device industries in the U.S., ensuring that industrial processes meet safety and efficacy standards.
- EU MDR (European Union Medical Device Regulation):
- Regulates the production and distribution of medical devices in the EU, requiring stringent quality control and risk management processes.
- CFR Title 49 (Transportation of Hazardous Materials):
- U.S. regulations governing the safe transportation of hazardous materials, including those used or produced in industrial processes.
8. Energy Efficiency Standards
- ISO 50001 (Energy Management Systems):
- An international standard that provides a framework for establishing energy management best practices, improving energy efficiency, and reducing energy costs.
- ASHRAE Standards:
- Standards related to energy efficiency in heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration systems, often used in industrial settings.
9. Materials and Equipment Standards
- ASTM International (American Society for Testing and Materials):
- Publishes standards for materials, products, systems, and services, including those used in industrial processes (e.g., ASTM A36 for structural steel).
- BS (British Standards):
- Standards for materials and equipment used in the UK and internationally, covering a wide range of industrial applications.
10. International Standards
- ISO Standards:
- Various ISO standards apply to industrial process solutions, covering quality, safety, environmental management, and more.
- EN Standards (European Norms):
- European standards that often align with ISO standards but are specifically tailored to the EU regulatory environment.
Compliance with these standards and regulations ensures that industrial process solutions are safe, efficient, and environmentally responsible while also meeting the legal and quality requirements of the industries they serve.


 Automation System
Automation System  Energy Engineeing
Energy Engineeing  Instrumentation System
Instrumentation System  Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical Engineering  Piping Technologies
Piping Technologies  Transportations
Transportations  Manufacturing
Manufacturing  Training Material
Training Material 



















 Instrumentation Services
Instrumentation Services