ASTM A276 Standard Specification for Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes
Contents

Contents1 I. Introduction API 1169 standard2 II. Background and Development of API 11692.1 Historical Context2.2 Industry Collaboration and Stakeholder Involvement2.3 Objectives of API 11692.4 Evolution of the Standard2.5 Integration with Global Standards3 III. Key Components of API 1169 Standard3.1 1. General Pipeline Construction Practices3.2 2. Safety3.3 3. Environmental and Regulatory Compliance3.4 4. Inspection Practices and […]

Contents1 What is check valve pressure drop ?2 Check valve pressure drop calculation formula3 What is the typical pressure drop for a check valve?4 How to prevent check valve pressure drop5 Check valve pressure drop chart What is check valve pressure drop ? The pressure drop across a check valve refers to the decrease in […]

Contents1 Introduction to SUS 304 Stainless Steel1.0.1 Historical Background1.0.2 Common Uses2 Composition and Properties of SUS 304 Stainless Steel2.1 Chemical Composition2.2 Physical and Mechanical Properties2.3 Comparison with Other Stainless Steel Grades3 Manufacturing Process of SUS 304 Stainless Steel3.1 Melting and Casting3.2 Forming and Shaping3.3 Heat Treatment3.4 Finishing Processes4 Applications of SUS 304 Stainless Steel4.1 Culinary […]
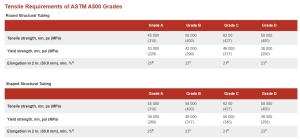
Contents1 Introduction and Overview of ASTM A5002 Scope of ASTM A5002.1 Types of Structural Tubing Covered2.2 Comparison with Other Standards2.3 Applications and Industries3 Chemical Requirements of ASTM A5004 5 Tensile Requirements of ASTM A500 Grades6 A500 Outside Dimensional Tolerances for Square & Rectangular Steel tubing7 Manufacturing Process for ASTM A500 structural tubing7.1 Cold-Forming Process7.2 Welding […]

Contents1 Introduction and Overview of ASTM A2692 Scope of ASTM A2693 Material Specifications outlined in ASTM A2693.1 Austenitic Stainless Steel Grades3.2 Chemical Properties3.3 Mechanical Properties3.4 Durability and Reliability3.5 Applications4 Manufacturing Process4.1 Melting and Casting4.2 Forming4.3 Welding (for Welded Tubes)4.4 Final Heat Treatment4.5 Challenges and Considerations5 Conclusion Introduction and Overview of ASTM A269 ASTM A269 is […]

Contents1 Introduction and Overview of ASTM D42362 Scope and Relevance of ASTM D42363 Requirements of ASTM D42363.1 Labeling Requirements3.2 Understanding “Chronic Health Hazard”3.3 Risk Assessment for Labeling3.4 Role of Toxicologists4 Labeling and Information4.1 Labeling Requirements Under ASTM D42364.1.1 Hazard Warnings4.1.2 Precautionary Statements4.1.3 Safe Use Instructions4.2 Importance of Clear and Accessible Information4.3 Comparison with Other Labeling […]

Contents1 Overview of API 1163 standard2 Importance of API 1163 standard in Pipeline Integrity Management3 Scope and Purpose of API 1163 standard3.1 What API 1163 standard Covers3.2 Goals of the API 1163 Standard4 Technical Specifications Inspection of API 1163 standard4.1 Inspection Technologies Covered4.2 Qualification Requirements for Inspection Systems5 Operational Guidelines API 1163 standard5.1 API 1163 standard […]

Contents1 Introduction1.0.1 Historical Context2 Technical Scope of API Standard 11042.1 Welder Qualification and Certification2.2 Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS)2.3 API Standard 1104 : Inspection and Testing2.4 Safety and Environmental Considerations3 Compliance and Regulatory Impact4 Case Studies and Practical Applications5 Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of API Standard 11045.1 Key Takeaways:5.2 Looking Ahead:5.3 Final Reflections Introduction API Standard […]

Contents1 AWS welding standards introduction.2 The AWS standards of specialized welding applications2.1 Automotive Welding2.2 Sheet Metal and Piping2.3 Industrial and Specialized Welding2.4 Robotic and Aerospace Welding2.5 Hygienic Welding3 AWS standards welding procedures3.1 1. Welding Procedure Specification (WPS)3.2 2. Procedure Qualification Record (PQR)3.3 3. Welder Performance Qualification (WPQ)3.4 Key AWS Standards Related to Welding Procedures:3.5 Importance […]

Contents1 What is welding codes or welding standards ?2 2.1 Key Elements of Welding Codes and Standards:2.2 Examples of Welding Codes and Standards Organizations:3 The list of welding standards3.1 American Welding Society (AWS)3.2 American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME)3.3 American Petroleum Institute (API)3.4 International Organization for Standardization (ISO)3.5 European Committee for Standardization (CEN)3.6 Other Standards […]


 Automation System
Automation System  Energy Engineeing
Energy Engineeing  Instrumentation System
Instrumentation System  Mechanical Engineeing
Mechanical Engineeing  Piping Technologies
Piping Technologies  Transportations
Transportations  Manufacturing
Manufacturing  Training Material
Training Material 
