Schedule 40 pipe dimensions : schedule 40 steel pipe and schedule 40 pvc pipe
Contents
- 1 What is schedule 40 pipe?
- 2 Schedule 40 pipe dimensions
- 3 Table schedule 40 pipe dimensions from 1/4 in to 20 in
- 4 Schedule 40 steel pipe
- 5 Dimensions schedule 40 steel pipe from 1/4 to 20in
- 6 Schedule 40 pvc pipe
- 7 Table schedule 40 pvc pipe dimension from 1/4 in to 20 in
- 8 Schedule 40 pipe dimensions standards
Schedule 40 pipe dimensions

Contents1 I. Introduction API 1169 standard2 II. Background and Development of API 11692.1 Historical Context2.2 Industry Collaboration and Stakeholder Involvement2.3 Objectives of API 11692.4 Evolution of the Standard2.5 Integration with Global Standards3 III. Key Components of API 1169 Standard3.1 1. General Pipeline Construction Practices3.2 2. Safety3.3 3. Environmental and Regulatory Compliance3.4 4. Inspection Practices and […]
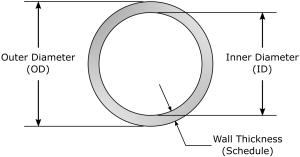
Contents1 What is pipe schedule chart?1.1 Definition and Overview1.2 Importance in Various Industries2 Table of pipe schedule charts3 History of Pipe Scheduling Evolution3.1 Early Beginnings3.2 Move Towards Standardization3.3 Role of Standardization Bodies3.4 Key Developments in Pipe Scheduling3.5 Modern Implications4 Understanding Pipe Sizes and Schedules4.1 Nominal Pipe Size (NPS)4.2 Pipe Schedule Numbers4.3 Thickness, Diameter, and Pressure […]

Contents1 Introduction and Overview of ASTM D42362 Scope and Relevance of ASTM D42363 Requirements of ASTM D42363.1 Labeling Requirements3.2 Understanding “Chronic Health Hazard”3.3 Risk Assessment for Labeling3.4 Role of Toxicologists4 Labeling and Information4.1 Labeling Requirements Under ASTM D42364.1.1 Hazard Warnings4.1.2 Precautionary Statements4.1.3 Safe Use Instructions4.2 Importance of Clear and Accessible Information4.3 Comparison with Other Labeling […]

Contents1 Introduction ASTM A531.1 Historical Context1.2 Types of Pipes and Applications2 Scope and Classification of ASTM A532.1 Scope of ASTM A532.2 Classification of ASTM A53 Pipes2.3 Versatility and Applications3 Material and Manufacture3.1 Material Composition and Grades3.2 Manufacturing Processes3.2.1 Type F (Furnace Butt-Welded)3.2.2 Type E (Electric-Resistance Welded)3.2.3 Type S (Seamless)3.3 Importance of Material Quality and Manufacturing […]

Contents1 Introduction ASTM E1192 Scope and Purpose of ASTM E1193 Test Methods and Procedures3.1 Standard Fire Test Furnace and Conditions3.2 Preparation for the Fire Tests3.3 Execution of the Fire Tests3.4 Evaluation of the Fire Tests3.5 Temperature Measurements and Structural Integrity3.6 Conclusion4 Materials and Construction Types Covered4.1 Steel Constructions4.2 Concrete Constructions4.3 Timber Constructions4.4 Modern and Composite […]

Contents1 Introduction ASTM B2092 Materials and Scope3 Technical Specifications3.1 Chemical Compositions3.2 Mechanical Properties3.3 Tolerances3.4 Technical Terms and Definitions3.5 Classifications4 Manufacturing Process and Quality Control4.1 Manufacturing Process4.2 Quality Control Measures4.3 Case Studies of Non-Compliance5 Applications and Case Studies5.1 Aerospace Industry5.2 Automotive Industry5.3 Construction and Architecture5.4 Renewable Energy Sector5.5 Marine Industry5.6 Electronics Industry6 Conclusion Introduction ASTM B209 […]

Contents1 ASTM A240 Introduction2 Scope and General Description3 ASTM A240 Material Grades and Classification3.0.1 ASTM A240 Austenitic Stainless Steels3.0.2 ASTM A240 Ferritic Stainless Steels3.0.3 ASTM A240 Duplex Stainless Steels3.0.4 ASTM A240 Martensitic Stainless Steels4 Chemical Composition4.0.1 Key Elements and Their Roles4.0.2 Grade-Specific Chemical Requirements4.1 Impact on Mechanical Properties5 Mechanical Properties5.0.1 Yield Strength5.0.2 Tensile Strength5.0.3 Elongation5.0.4 […]

Contents1 Introduction to ASTM E841.1 Overview and Significance1.2 Historical Development1.3 Purpose and Scope2 Understanding the Technical Aspects of ASTM E842.1 Test Procedure Overview2.2 Equipment and Setup2.3 Test Execution and Data Collection2.4 Interpreting the Results3 Applications of ASTM E84 in Building Safety and Material Selection3.1 Role in Building Codes and Regulations3.1.1 Influence on Material Development and […]

Contents1 API 2000 Standard : Venting Atmospheric and Low-Pressure Storage Tanks2 Historical Context of API 2000 standard3 Technical Overview of API 2000 standard3.1 Venting Requirements3.2 Design Considerations3.3 Calculations and Methodologies3.4 Implementing API 2000 standard3.5 Industry Applications3.6 Safety Implications3.7 Regulatory Compliance4 Case Studies4.1 Successful Implementations4.2 Learning from Failures5 Conclusion API 2000 Standard : Venting Atmospheric and […]

Contents1 What is Pipe Painting Specifications?2 Paint Used for Piping3 Pipe painting specifications4 Pipe painting in industry applications4.1 1. Oil & Gas Industry4.2 2. Chemical Industry4.3 3. Water and Wastewater Industry4.4 4. Marine and Offshore Industry4.5 5. Construction and Infrastructure4.6 6. Power Generation Industry4.7 7. Food and Beverage Industry5 Pipe painting standards for each industry5.1 […]


 Automation System
Automation System  Energy Engineeing
Energy Engineeing  Instrumentation System
Instrumentation System  Mechanical Engineeing
Mechanical Engineeing  Piping Technologies
Piping Technologies  Transportations
Transportations  Manufacturing
Manufacturing  Training Material
Training Material 
